You are a non-European company and you use Incoterm DDP for your sales to France and Incoterm EXW for your purchases from France? You are likely to act as an IOR/EOR on French territory and to have certain VAT obligations.
Definition of an Importer of Record (IOR) and an Exporter of Record (EOR)
What is an Importer of record (IOR) ?
TheImporter of Records (IOR) is a local or foreign company legally responsible for importing goods into France. The IOR is responsible for filing customs import documents (including licenses and permits), as well as the payment of import duties and taxes.
What is an Exporter of record (EOR) ?
The Exporter Of Records (IOR) is a local or foreign company legally responsible for the export of goods to France. He is responsible for the filing of customs export documents (including licenses and permits), as well as the risks associated with exporting (late delivery, financial and penal risks in case of violation of customs procedures, etc.).
What are DDP and EXW incoterms?
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP)
With the use of the DDP Incoterm, the seller bears all transportation costs, customs clearance (including payment of duties and taxes) and all risks until the goods are made available to the customer.
The Incoterm DDP is the one that places the least responsibility on the buyer.
Incoterm EXW (Ex-works)
With the use of the EXW Incoterm, the seller leaves all transportation costs, customs clearance (including the payment of duties and taxes) and all risks to the final destination to the buyer.
The EXW Incoterm places the least amount of responsibility on the seller.
Examples of use of DDP/EXW incoterms, IOR/EOR concepts and their impact on VAT
DDP sales by a foreign company in France
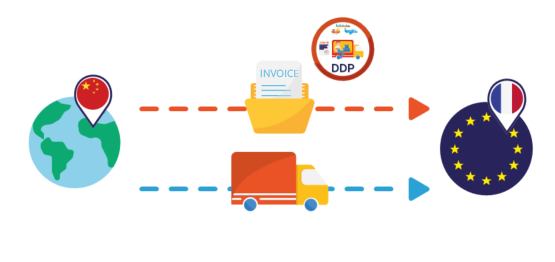
A Chinese company sells according to the Incoterm DDP to its French customers. The use of the Incoterm DDP, as we have seen, implies for the salesman that he has in his load the customs clearance in France of the goods as well as the payment of the rights and taxes to the importation.
- Advantages: the buyer does not take any risk and does not have to deal with customs formalities and unforeseen transportation issues. Moreover, the use of this Incoterm allows the buyer to be aware at the time of purchase of the totality of the costs and has no hidden and additional charges. Using the DDP makes life easier for your customers!
- Customs impacts: The Chinese seller acts as an IOR on the import customs documents. He will have to take care of the customs formalities on import in France and have a European EORI number.
- VAT impacts: By acting as an importer in France, it is the responsibility of the Chinese company to pay import duties and taxes (including VAT).
As of January 1, 2022, import VAT can no longer be paid at customs and must be subject to a reverse charge of import VAT via a French VAT return (CA3).
Therefore, the Chinese company must register for VAT in France through a French fiscal representative and self-assess the import VAT.
More about us

To learn more about the new obligations for foreign companies acting as importers in France as of January1, 2022, check out our dedicated blog: ATVAI 2022: obtaining a VAT number becomes mandatory for importers.
Setting up of a storage of goods in France by a foreign company

An American company wishes to set up a stock of goods in France in order to ensure the deliveries of its customers in Europe.
- Advantages: by setting up a storage facility in France, the American company is closer to its customers and guarantees fast delivery. Moreover, the American company can make grouped shipments of goods instead of making piecemeal deliveries, which greatly limits the number of customs formalities for importing into France and thus reduces the related costs !
- Customs impacts : the American seller acts as an IOR on the import customs documents. He will have to take care of the customs formalities on import in France and have a European EORI number.
- VAT impacts: acting as an importer in France, the US company must pay import duties and taxes (including VAT) .
Therefore, the American company must register for VAT in France in France through a French tax representative and self-assess the import VAT.
EXW purchase by a foreign company from a French supplier
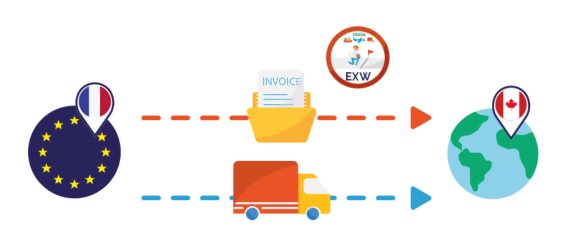
A Canadian company purchases goods from a French supplier under the EXW Incoterm.
- Advantages: As transport and formalities are managed by the buyer, he has full visibility on the logistics and delivery process.
- Customs Impacts: The Canadian buyer takes care of the customs formalities upon export. Since 2020, companies not established in the Customs Territory of the Union (TDU) can no longer act as exporters in the customs sense. The company must designate an operator established in the TDU to act in its place as exporter. In practice, this may be his VAT tax representative.
To learn more about it, visit our dedicated blog here
- VAT impacts : By taking charge of the customs on export to France, the American company must, via its fiscal representative, declare an export of goods on its French VAT return (CA3). It can invoice its customer without VAT under Article 262 I of the General Tax Code (CGI).
Cross-trade (country of departure France with delivery in Switzerland)
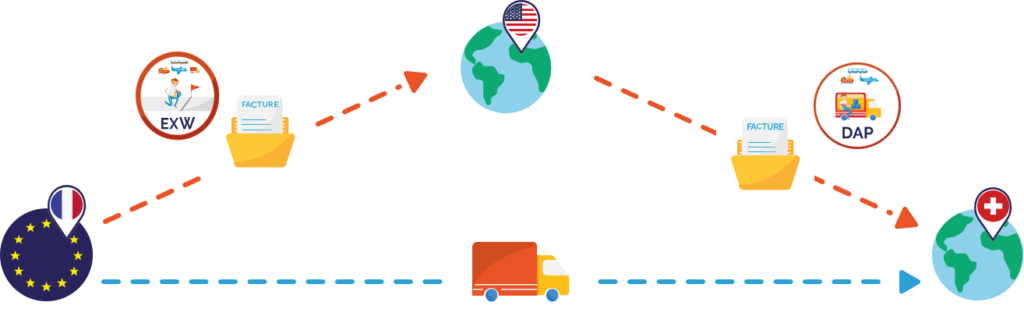
The American company carries out international trade and buys from French suppliers batches of goods that it resells to a Swiss company. The incoterms used are, for purchase EXW and for resale DAP.
- Advantages : The cross-trade allows the American company to make a margin on this buy-sell. The direct delivery between the supplier and the final customer makes it possible to reduce the delivery times, to save transport costs and not to multiply the customs formalities to be established and customs duties to be paid. For the French supplier, he is freed from export obligations thanks to the use of the EXW incoterm and the end customer is only in charge of customs obligations upon import into Switzerland. The U.S. buyer-reseller assumes the remaining obligations.
- Customs Impacts: The U.S. seller takes care of the customs formalities for export. Since 2020, companies not established in the Customs Territory of the Union can no longer act as an exporter in the customs sense. The company can designate an operator established in the TDU to act in its place as an exporter. In practice, this may be his VAT tax representative.
- VAT impacts : By taking charge of the customs at the export in France (Purchase at the conditions of departure EXW and resale in DAP), the American company must, through its fiscal representative, declare an export of goods on its French VAT return (CA3). It can invoice its customer without VAT in accordance with article 262 I of the CGI. It can also directly deduct the French VAT paid to its French supplier on its French VAT return (CA3).
To learnmore, read our dedicated blog: New VAT exemption conditions for exports as of October 1, 2020
Contact us:

Are you setting up new international operations and would like to know the consequences in terms of VAT? Don’t wait any longer and subscribe to our VAThotline offer.